
The disadvantages of management software include:
- High Cost – Many management software solutions require significant financial investment, including licensing fees, customization costs, and maintenance expenses.
- Complex Implementation – Deploying and integrating management software can be time-consuming and may require specialized training for employees.
- Security Risks – Storing sensitive business data on digital platforms increases the risk of cyber threats, data breaches, and hacking.
- Limited Flexibility – Some management software may not be easily customizable or adaptable to a company's unique workflows and needs.
- Dependence on the Vendor – Businesses often rely on the software provider for updates, support, and troubleshooting, which can lead to operational bottlenecks if the vendor is unresponsive.
- Learning Curve – Employees may require extensive training to fully utilize the software, leading to decreased productivity during the transition period.
- Potential Compatibility Issues – Integrating the software with existing tools and systems may be challenging, leading to inefficiencies or additional costs for custom integrations.
Would you like a more detailed analysis of any specific point?
相关问答FAQs:
What are the disadvantages of management software?
Management software has become an essential tool for businesses of all sizes, offering numerous benefits such as improved efficiency, streamlined communication, and enhanced data management. However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks that can accompany the implementation of such systems. Below are some key disadvantages associated with management software.
-
High Initial Costs: The adoption of management software often involves significant upfront costs. This includes the purchase of licenses, hardware upgrades, and potential consulting fees for implementation. For small businesses or startups, these expenses can strain budgets and may not yield immediate returns on investment.
-
Complexity and Learning Curve: Many management software solutions are sophisticated and feature-rich, which can lead to a steep learning curve for users. Employees may require extensive training to navigate the software effectively, and this process can be time-consuming and may temporarily disrupt normal business operations.
-
Dependence on Technology: Relying heavily on management software can create a dependency on technology. If the software experiences downtime, bugs, or other technical issues, it can halt business operations and lead to lost productivity. Moreover, businesses may become vulnerable to cyber threats if proper security measures are not in place.
-
Customization Challenges: While many management software solutions offer customizable features, tailoring the software to meet specific business needs can be complex and costly. Over-customization can lead to complications in upgrades and maintenance, as well as potential compatibility issues with other systems.
-
Data Security Concerns: Storing sensitive business data within management software raises valid concerns regarding data security. Even reputable software providers can fall victim to data breaches, exposing sensitive information. Businesses must invest in robust security measures and remain vigilant in monitoring potential threats.
-
Resistance to Change: Implementing new management software may encounter resistance from employees accustomed to existing processes. Change management is crucial to ensure buy-in from staff and facilitate a smooth transition. Without proper change management strategies, the software may not be utilized to its full potential.
-
Overcomplication of Processes: Some management software can overcomplicate workflows by introducing unnecessary features that may not align with the organization’s needs. This can lead to confusion among employees and detract from the primary objectives of improving efficiency and productivity.
-
Vendor Lock-In: Once a business commits to a specific management software solution, it may face challenges in switching to another provider in the future. Vendor lock-in can limit flexibility and choice, making it difficult to adapt to changing business requirements or to take advantage of new technologies.
-
Limited Scalability: While many management software solutions claim to be scalable, not all can handle rapid growth or increased demand. Businesses must carefully assess the scalability of a software solution before implementation to ensure it can grow alongside the organization without significant upgrades or replacements.
-
Potential for Data Loss: Relying on management software for data storage raises concerns about data loss due to software failure, accidental deletion, or insufficient backup measures. Organizations must establish comprehensive data backup protocols to mitigate this risk.
In conclusion, while management software offers numerous advantages, it is crucial for businesses to be aware of the potential disadvantages. By carefully weighing the pros and cons, organizations can make informed decisions about the software they choose to implement and how to maximize its benefits while minimizing its drawbacks.
How can businesses mitigate the disadvantages of management software?
To effectively address the disadvantages of management software, businesses can adopt several strategies:
-
Conduct Thorough Research: Before selecting a management software solution, businesses should conduct comprehensive research to understand their specific needs and evaluate different options. This includes reading reviews, seeking recommendations, and requesting demos to ensure the software aligns with organizational goals.
-
Implement Change Management Strategies: To ease the transition to new software, businesses should implement change management strategies. This includes involving employees in the selection process, providing training sessions, and creating a supportive environment that encourages feedback and adaptation.
-
Invest in Training: Providing ongoing training and support for employees is essential to maximize the benefits of management software. This can include workshops, tutorials, and access to resources that help employees become proficient in using the software.
-
Regularly Review and Update Systems: Businesses should regularly review their management software to ensure it continues to meet their evolving needs. This includes evaluating system performance, identifying areas for improvement, and upgrading software as necessary.
-
Prioritize Data Security: Implementing robust data security measures is critical to safeguarding sensitive information. Businesses should invest in encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect their data from breaches.
-
Create Backup Protocols: Establishing comprehensive backup protocols is essential to mitigate the risk of data loss. Businesses should implement automated backups and regularly test recovery processes to ensure data integrity.
By proactively addressing the disadvantages associated with management software, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency while minimizing potential risks.
What are some common features of management software?
Management software typically includes a variety of features designed to support business operations. Some common features include:
-
Project Management Tools: Many management software solutions offer project management functionalities, allowing teams to plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively. Features may include task assignment, progress tracking, and collaboration tools.
-
Time Tracking: Time tracking features enable businesses to monitor employee productivity and manage resources efficiently. This can help in project planning and ensure accurate billing for client work.
-
Document Management: Management software often includes document management capabilities, allowing users to store, share, and collaborate on documents securely. This feature enhances organization and accessibility.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Many management software solutions incorporate CRM functionalities to help businesses manage customer interactions, track sales leads, and analyze customer data.
-
Reporting and Analytics: Reporting and analytics features enable businesses to generate insights from data collected through the software. This can help in decision-making and identifying trends to improve performance.
-
Integration Capabilities: Effective management software should offer integration capabilities with other tools and systems, allowing businesses to streamline processes and enhance functionality.
-
User Access Controls: User access controls help businesses manage permissions and ensure that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized personnel.
-
Mobile Access: Many modern management software solutions provide mobile access, allowing employees to manage tasks and communicate with team members from anywhere, increasing flexibility and productivity.
-
Automated Workflows: Automation features can streamline repetitive tasks and improve efficiency. This includes automating notifications, approvals, and reporting processes.
-
Collaboration Tools: Effective collaboration tools facilitate communication among team members, allowing for real-time updates, shared calendars, and messaging capabilities.
By understanding the common features of management software, businesses can make informed decisions about which solution best meets their operational needs.
In conclusion, while management software offers numerous advantages, it is essential for businesses to recognize and address its potential disadvantages. By implementing strategies to mitigate risks and selecting software with the right features, organizations can enhance their efficiency and effectiveness in achieving their goals.
For those seeking a reliable business management system, consider trying out a platform that offers a free trial for a hands-on experience:
Explore over 100 free templates for business management systems that can be used online without the need for downloads:

 阅读时间:7 分钟
阅读时间:7 分钟  浏览量:6984次
浏览量:6984次

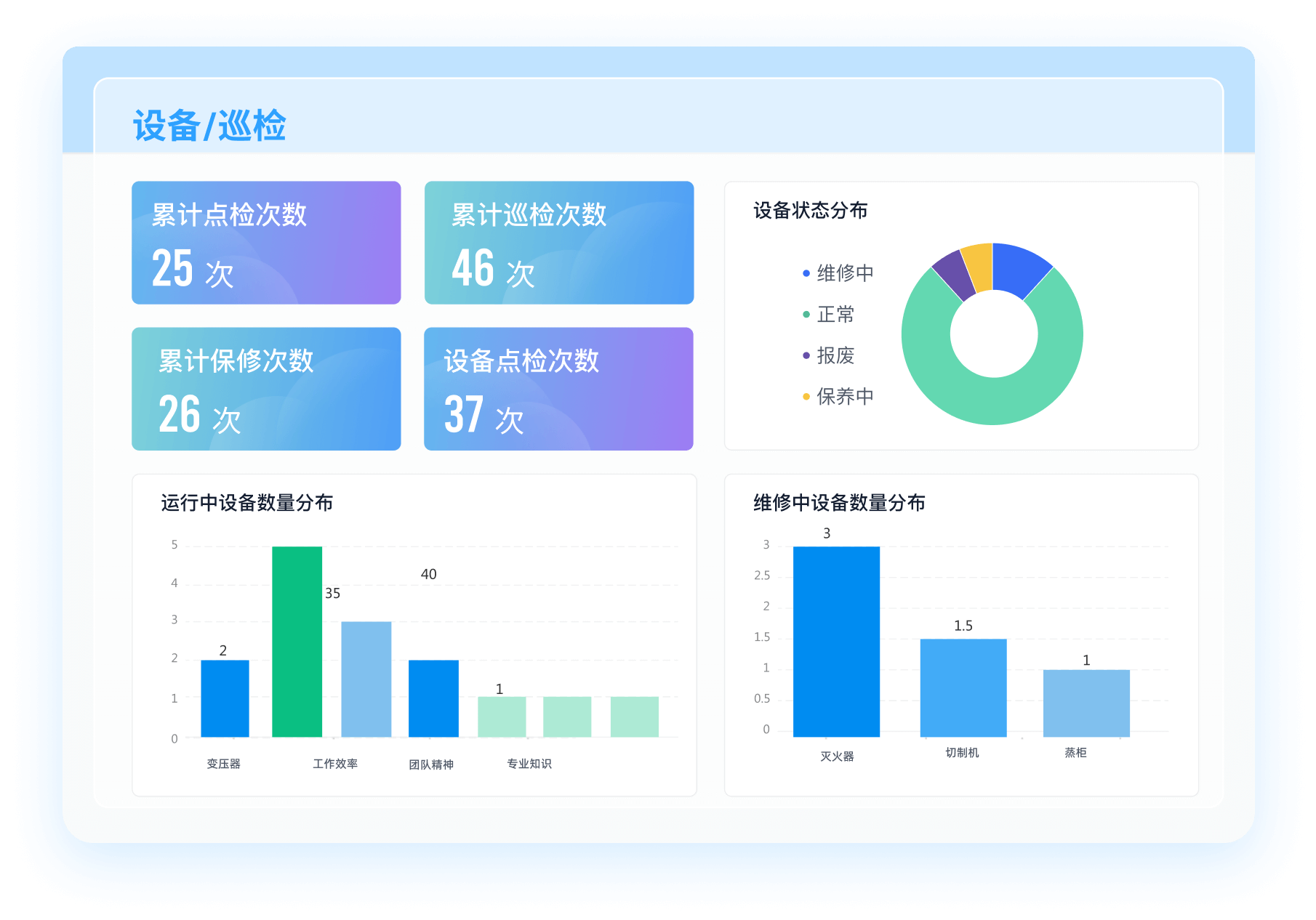
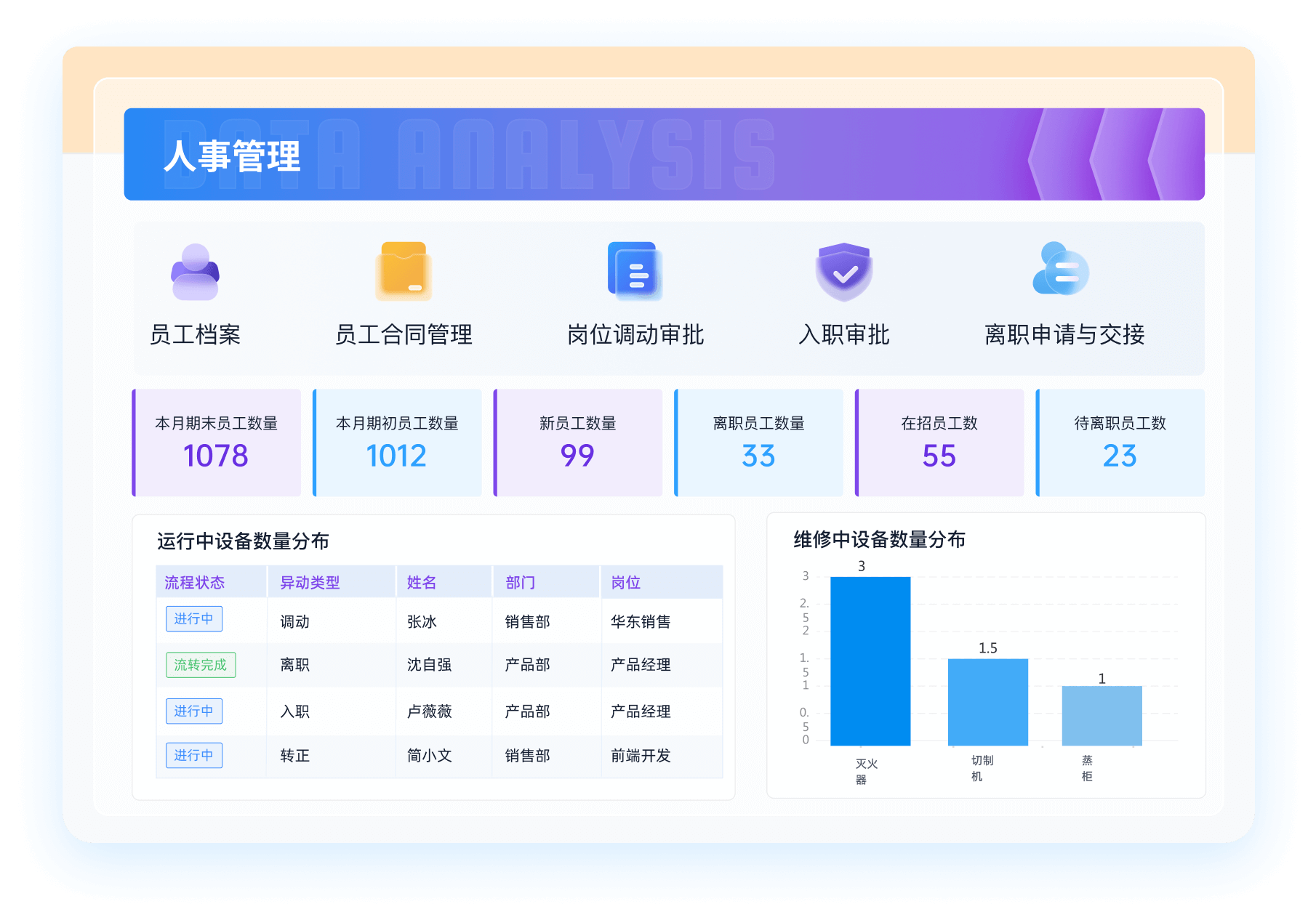
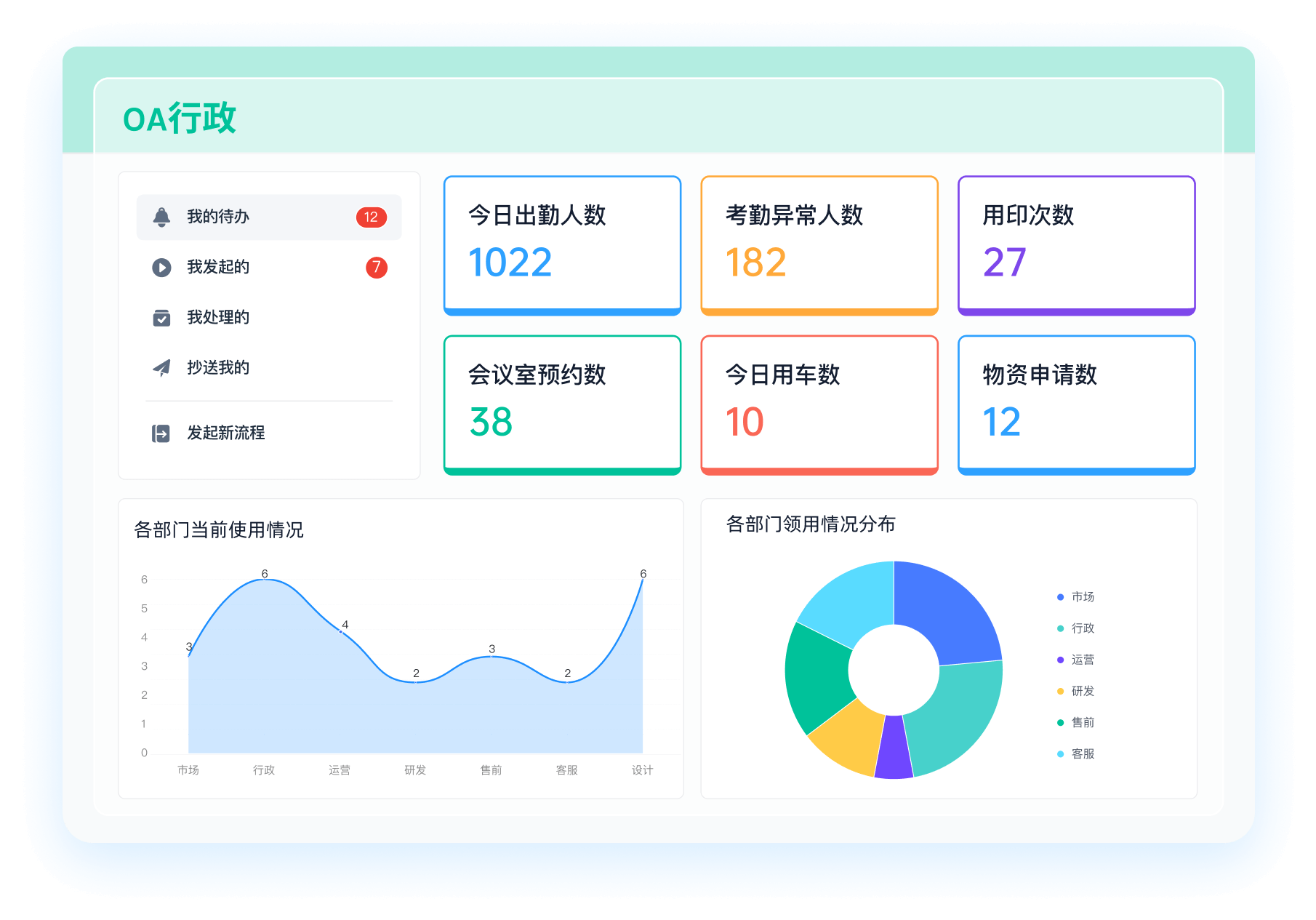
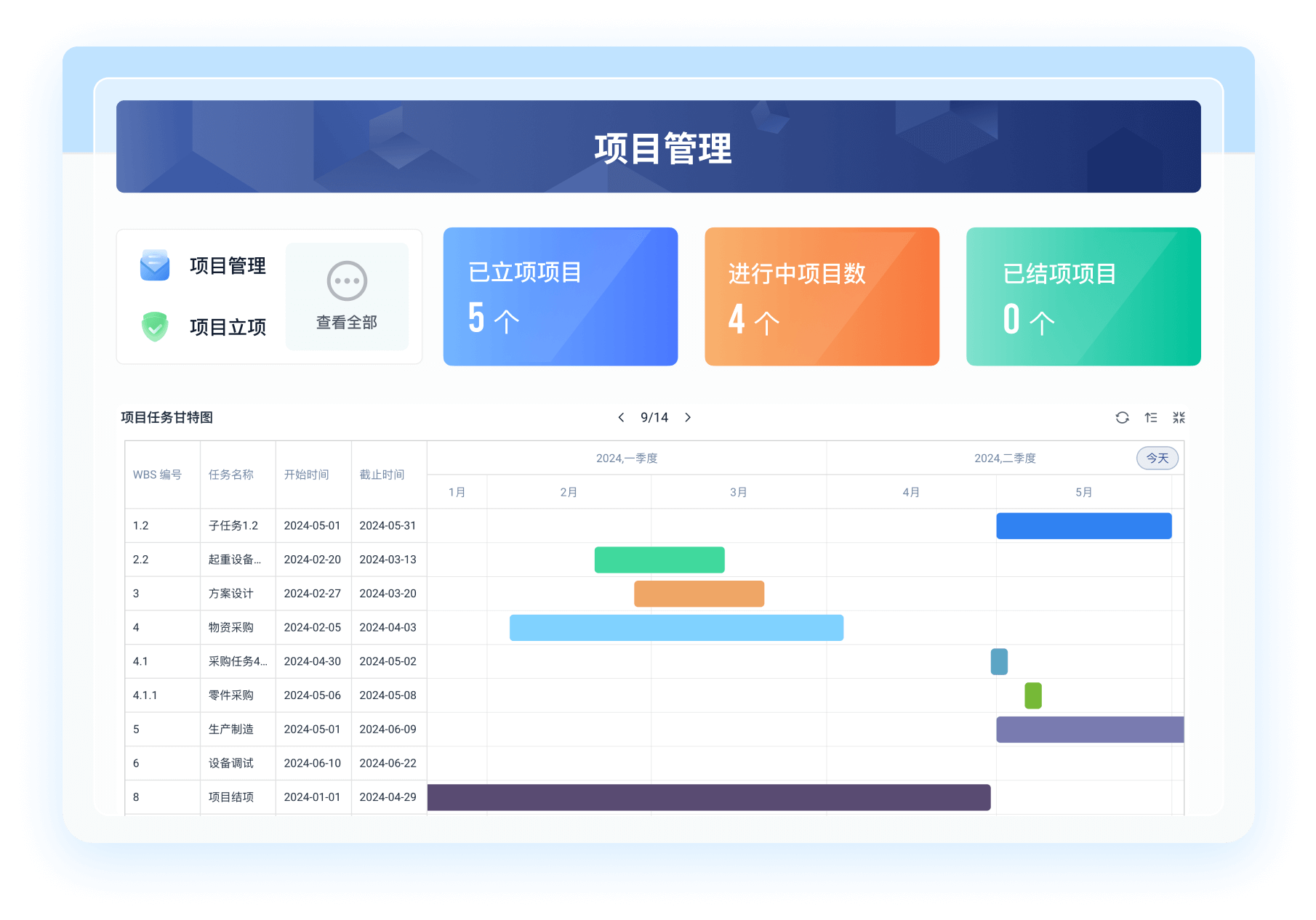
































































 《零代码开发知识图谱》
《零代码开发知识图谱》
 《零代码
新动能》案例集
《零代码
新动能》案例集
 《企业零代码系统搭建指南》
《企业零代码系统搭建指南》









