
To create an inventory table in Excel in English, you need to follow these steps: open Excel, create columns for Item Name, Item Description, Quantity, Unit Price, and Total Value, input your inventory data, use formulas to calculate total values, and apply formatting for clarity and readability. One key point is to use Excel’s built-in functions to automate calculations, which can significantly reduce manual work and errors. For example, by using the SUM function, you can quickly add up quantities or values, while the VLOOKUP function helps in retrieving information based on specific criteria.
I. OPENING EXCEL AND CREATING COLUMNS
When you start by opening Excel, your first task is to set up the fundamental structure of your inventory table. Begin with creating a new workbook. This can be done by selecting 'File' from the top menu, then 'New', and choosing a blank workbook. Once your new workbook is open, you will create column headers to organize your data. The essential columns for an inventory table typically include:
- Item Name: The name or title of the item.
- Item Description: A detailed description of the item.
- Quantity: The number of units available in stock.
- Unit Price: The cost of a single unit.
- Total Value: The total monetary value of the item in stock.
To create these columns, simply click on the first cell of each column (starting from A1 for the first column) and type in the respective header names. Ensuring that your headers are clear and descriptive will help in maintaining a well-organized and easy-to-navigate inventory table.
II. INPUTTING INVENTORY DATA
After setting up your columns, the next step is to input your inventory data. Populate your table with the relevant information for each item. For instance, under the 'Item Name' column, enter the names of all the items in your inventory. In the 'Item Description' column, provide a brief but comprehensive description of each item. The 'Quantity' column should reflect the number of each item currently in stock. The 'Unit Price' column requires the price per unit of each item.
When entering data, ensure accuracy and consistency. Avoid using different formats for similar data, as this can lead to confusion and errors. For example, if you are recording quantities, decide whether to use whole numbers or decimals and stick to that format throughout the table.
III. USING FORMULAS TO CALCULATE TOTAL VALUES
One of the most powerful features of Excel is its ability to perform calculations automatically. To calculate the 'Total Value' for each item, you can use a simple formula. In the 'Total Value' column, enter a formula that multiplies the quantity of the item by its unit price. For instance, if the quantity is in cell C2 and the unit price is in cell D2, you would enter the formula =C2*D2 in cell E2.
Drag the fill handle (a small square at the bottom right corner of the selected cell) down the column to apply the formula to all rows in the 'Total Value' column. This action will automatically calculate the total value for each item based on the quantity and unit price you entered.
IV. APPLYING FORMATTING FOR CLARITY AND READABILITY
To make your inventory table more readable and visually appealing, apply formatting to your cells. Start by bolding your column headers to differentiate them from the rest of the data. You can also use different font colors or background colors to highlight important information.
Another useful formatting technique is to use conditional formatting. For example, you can set up conditional formatting to highlight cells in the 'Quantity' column that fall below a certain threshold, indicating low stock levels. To do this, select the cells in the 'Quantity' column, go to the 'Home' tab, click 'Conditional Formatting', and choose a rule that suits your needs.
Moreover, consider formatting the 'Unit Price' and 'Total Value' columns as currency. This can be done by selecting the cells, right-clicking, choosing 'Format Cells', and selecting 'Currency' from the list of options. Proper formatting not only improves the visual appeal of your table but also enhances data comprehension and reduces the likelihood of errors.
V. UTILIZING EXCEL FUNCTIONS FOR INVENTORY MANAGEMENT
Excel offers a variety of functions that can aid in managing your inventory more efficiently. The SUM function, for instance, can be used to calculate the total quantity of all items in stock. Simply select a cell where you want the total to appear, type =SUM(C2:Cn) (where C2 is the first cell in the 'Quantity' column and Cn is the last cell), and press Enter.
The VLOOKUP function is another powerful tool that helps retrieve specific information from your table based on a search criterion. For example, if you want to find the unit price of a particular item, you can use VLOOKUP to search for the item name and return the corresponding unit price. The formula =VLOOKUP("ItemName", A2:E100, 4, FALSE) will search for the item name in the first column (A2:A100) and return the value from the fourth column (Unit Price).
Additionally, the IF function can be used to create conditional statements. For example, you can use it to create alerts for low stock levels. An IF statement like =IF(C2<10, "Low Stock", "In Stock") in a new column can help you quickly identify items that need to be reordered.
VI. CREATING CHARTS AND GRAPHS
Visual representations of your inventory data can provide insights that are not immediately apparent from the raw numbers. Excel allows you to create various types of charts and graphs, such as bar charts, pie charts, and line graphs, to visualize your inventory data.
To create a chart, select the data you want to include, go to the 'Insert' tab, and choose the type of chart you want to create. For instance, a bar chart can be useful for comparing the quantities of different items, while a pie chart can show the proportion of each item in your total inventory.
Customize your charts by adding titles, labels, and legends. This can be done by clicking on the chart and using the 'Chart Tools' that appear in the toolbar. Well-designed charts can help you quickly identify trends and make informed decisions about your inventory management.
VII. USING PIVOT TABLES FOR ADVANCED ANALYSIS
Pivot tables are a powerful feature in Excel that allow you to summarize and analyze large amounts of data quickly. They can be particularly useful for inventory management, as they enable you to view your data from different perspectives and identify patterns and trends.
To create a pivot table, select your data range, go to the 'Insert' tab, and click 'PivotTable'. Choose where you want the pivot table to be placed (in a new worksheet or the existing one) and click 'OK'. In the PivotTable Field List, drag and drop fields into the Rows, Columns, Values, and Filters areas to customize your table.
For example, you can drag 'Item Name' to the Rows area, 'Quantity' to the Values area, and 'Category' (if you have one) to the Columns area. This setup will give you a summary of the quantities of each item by category. Pivot tables are highly flexible and can be adjusted as needed to provide the specific insights you require.
VIII. AUTOMATING INVENTORY UPDATES WITH MACROS
If you frequently update your inventory data, consider using macros to automate repetitive tasks. Macros are sequences of instructions that automate complex or repetitive tasks in Excel. They can save you a significant amount of time and reduce the risk of errors.
To create a macro, go to the 'View' tab, click 'Macros', and select 'Record Macro'. Give your macro a name and choose where to store it (in the current workbook or a personal macro workbook). Perform the actions you want to automate, and Excel will record them. When you're done, click 'Stop Recording'.
You can run your macro by going to the 'View' tab, clicking 'Macros', and selecting 'View Macros'. Choose the macro you want to run and click 'Run'. Macros can be edited in the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) editor if you need to make adjustments or add more complex functionality.
IX. SHARING AND COLLABORATING ON YOUR INVENTORY TABLE
Excel makes it easy to share your inventory table with others and collaborate in real-time. If you are using Excel Online or have a Microsoft 365 subscription, you can share your workbook with others by clicking the 'Share' button in the top right corner. Enter the email addresses of the people you want to share with and choose their permission level (view or edit).
Collaborators can make changes to the workbook, and you can see their updates in real-time. This feature is particularly useful for teams that need to manage inventory collectively, as it ensures that everyone has access to the most up-to-date information.
For added security, you can protect your workbook with a password. Go to the 'File' tab, click 'Info', and select 'Protect Workbook'. Choose 'Encrypt with Password' and enter a password. This will prevent unauthorized users from accessing your inventory data.
X. INTEGRATING EXCEL WITH OTHER TOOLS
Excel can be integrated with other tools and software to enhance your inventory management capabilities. For instance, you can use Excel with JianDaoyun, a cloud-based platform that allows you to create customized business applications without coding. By integrating Excel with JianDaoyun, you can automate data entry, generate reports, and even create mobile apps to manage your inventory on the go.
To integrate Excel with JianDaoyun, you can use their API or import/export features. This integration allows you to synchronize data between Excel and JianDaoyun, ensuring that your inventory information is always up-to-date and accessible from anywhere.
Additionally, Excel can be connected to databases, such as Microsoft Access or SQL Server, to pull in inventory data and perform more advanced analyses. This integration enables you to handle larger datasets and conduct more complex queries and reports.
Conclusion
Creating and managing an inventory table in Excel requires a combination of accurate data entry, effective use of formulas and functions, and thoughtful application of formatting and visualization tools. By leveraging Excel's powerful features, such as pivot tables, macros, and integrations with other tools like JianDaoyun, you can streamline your inventory management processes and make more informed business decisions. Excel's flexibility and versatility make it an ideal tool for handling inventory data, whether you're managing a small business or a large enterprise.
For more advanced solutions, you can explore JianDaoyun for creating customized applications tailored to your specific needs. JianDaoyun offers a range of features designed to enhance your inventory management capabilities, making it easier to track, update, and analyze your inventory data efficiently. For more information, visit the official website: https://s.fanruan.com/gwsdp;.
相关问答FAQs:
What is an Excel Inventory Sheet?
An Excel Inventory Sheet is a spreadsheet template designed to help businesses manage their inventory effectively. This sheet allows users to track stock levels, sales, orders, and more in a structured format. It typically includes columns for item names, descriptions, quantities on hand, reorder levels, prices, and total value. By using an Excel Inventory Sheet, businesses can maintain accurate records of their inventory, prevent stockouts, and streamline the ordering process. Moreover, this tool is particularly beneficial for small to medium-sized enterprises that may not have access to more complex inventory management software.
How to Create an Inventory Sheet in Excel?
Creating an inventory sheet in Excel is a straightforward process that requires just a few steps. Begin by opening Excel and creating a new workbook.
-
Set Up Your Columns: Label the first row with headers that represent the information you want to track. Common headers include Item ID, Item Name, Category, Quantity on Hand, Reorder Level, Supplier, Cost per Unit, and Total Value.
-
Input Your Data: Start populating the rows with your inventory items. Each item should have its own row, and you should fill in the details under each corresponding header.
-
Use Formulas for Calculations: To calculate the total value of your inventory, you can use a formula that multiplies the quantity on hand by the cost per unit. For instance, in the Total Value column, you would enter
=C2*H2(assuming C is Quantity and H is Cost per Unit). -
Conditional Formatting: To easily identify items that need to be reordered, apply conditional formatting to the Quantity on Hand column. Set rules that highlight cells in red when quantities fall below the reorder level.
-
Save Your Template: Once you are satisfied with your inventory sheet, save it as a template for future use. This way, you can update it regularly without starting from scratch.
By following these steps, you can create a functional inventory management tool that will help you keep track of your stock efficiently.
What are the Benefits of Using an Excel Inventory Sheet?
Utilizing an Excel Inventory Sheet offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes. One of the most significant benefits is the cost-effectiveness of using Excel, as it is often included in standard office software packages.
Another advantage is the flexibility and customization options available. Users can easily modify the template to suit their specific inventory needs, adding or removing columns and rows as required. This adaptability makes it suitable for a wide range of industries, from retail to manufacturing.
Excel's built-in formulas and functions enable businesses to automate calculations, reducing the risk of human error and saving time. Users can quickly assess stock levels, determine when to reorder, and analyze inventory turnover rates.
Furthermore, the ability to create charts and graphs in Excel allows businesses to visualize their inventory data, making it easier to identify trends and make informed decisions. The straightforward interface also means that employees with minimal training can use the sheet effectively.
In summary, an Excel Inventory Sheet is a practical tool for managing inventory, offering cost savings, customization, automation, and data visualization capabilities.
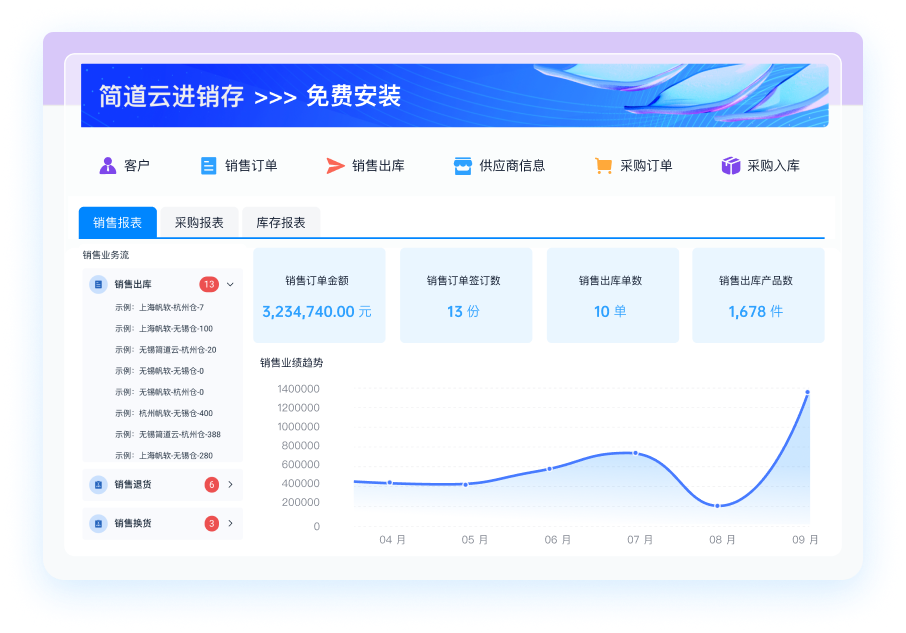
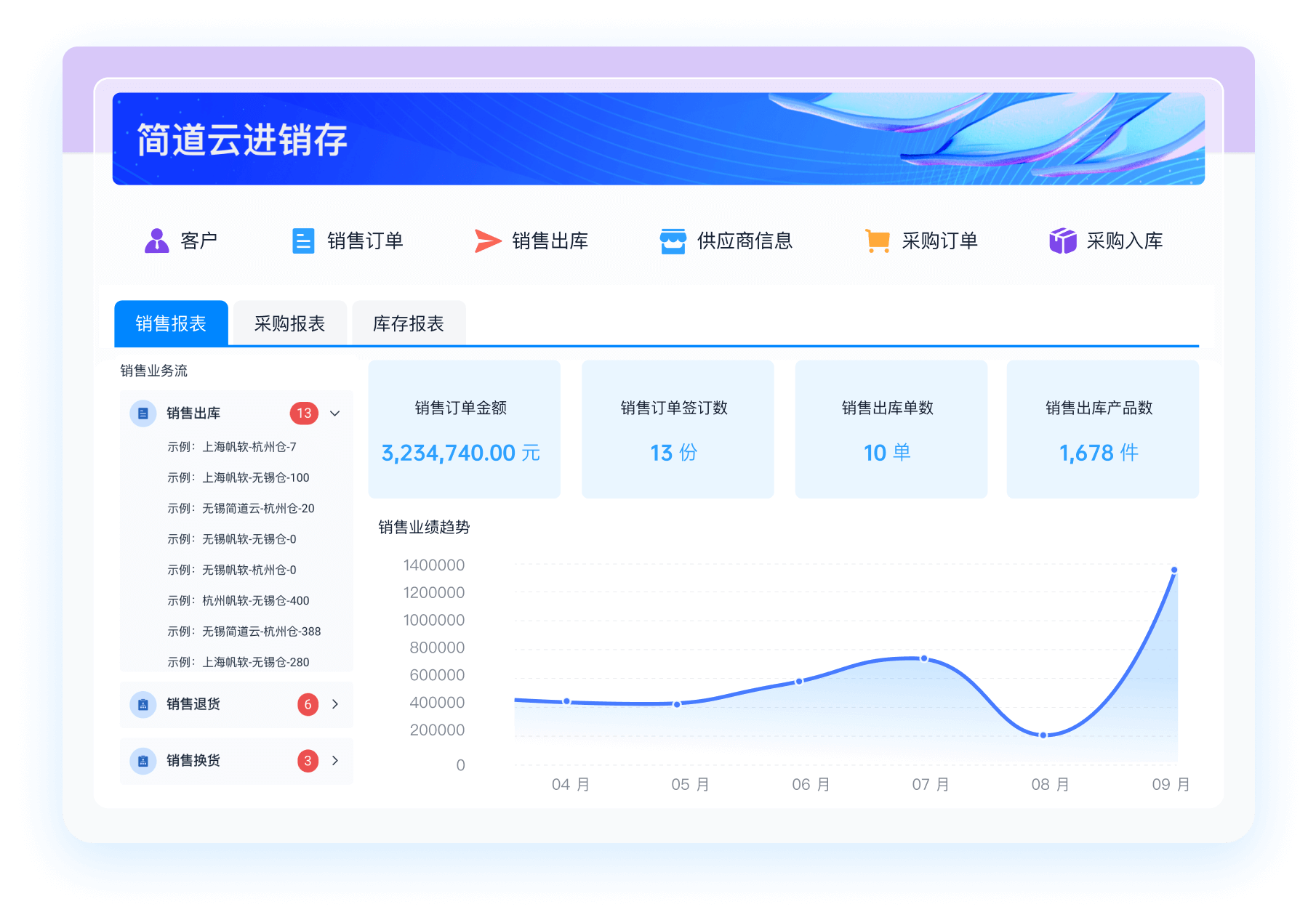
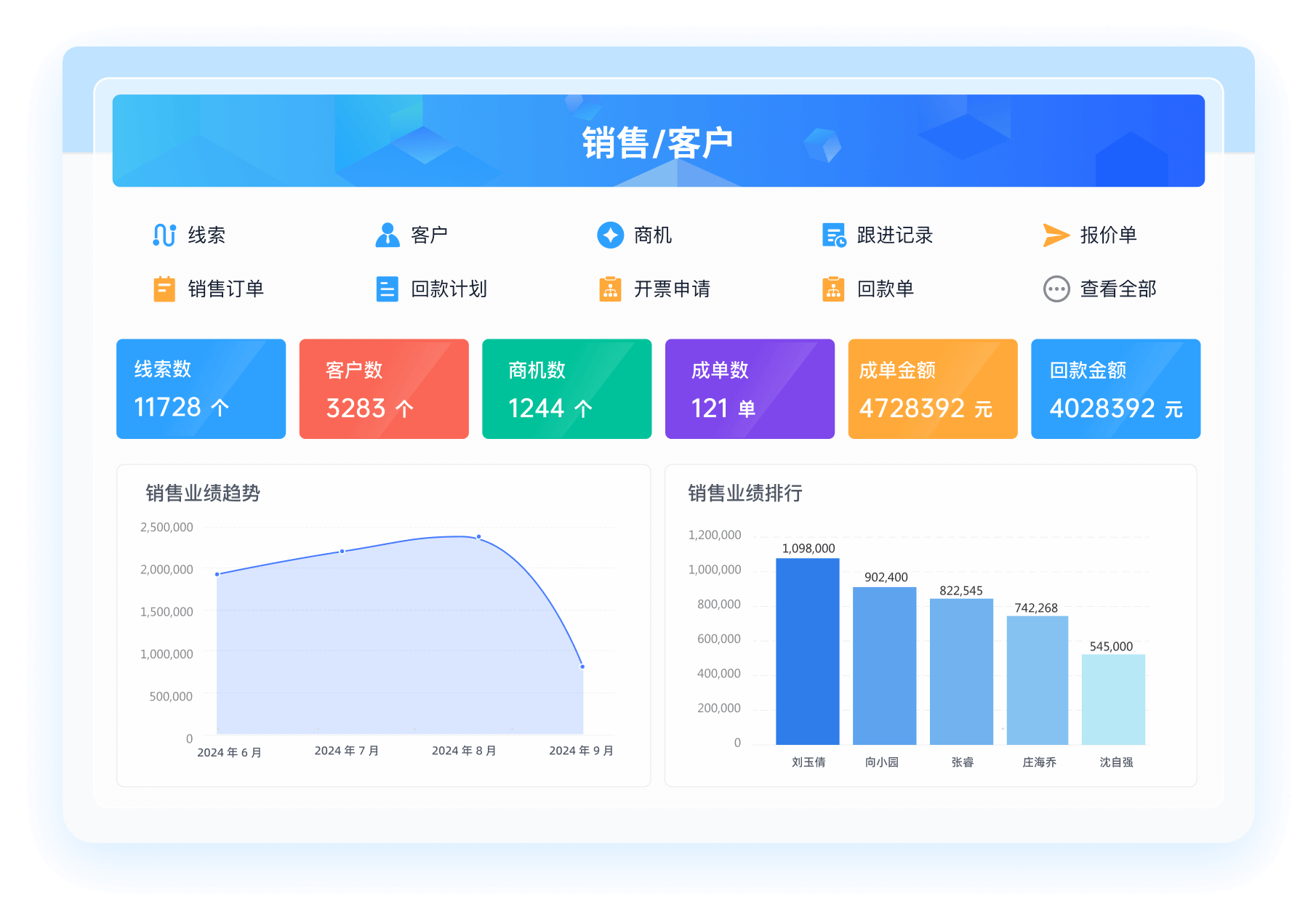
推荐100+企业管理系统模板免费使用>>>无需下载,在线安装:
地址: https://s.fanruan.com/7wtn5;

 阅读时间:8 分钟
阅读时间:8 分钟  浏览量:4483次
浏览量:4483次

































































 《零代码开发知识图谱》
《零代码开发知识图谱》
 《零代码
新动能》案例集
《零代码
新动能》案例集
 《企业零代码系统搭建指南》
《企业零代码系统搭建指南》









